Amniocentesis is done any time after the completion of the 16th week of pregnancy.
a) If you got a high-risk result from screening tests like double marker, quadruple marker, or NIPS test for chromosomal abnormalities.
b) If your scan showed an increased chance of your baby having a genetic or chromosomal disorder.
c) If you or your spouse have a higher risk of passing on an inherited abnormality, for example, Sickle cell disease or Thalassemia major.
d) If you had a previous pregnancy where your baby born with a genetic or chromosomal abnormality
Amniocentesis is a relatively safe procedure. However, complications can occur rarely, like miscarriage and preterm delivery, which can be 1 in 1000 procedures.
a) The test is done with the utmost sterile precautions
b) The first step of the Amniocentesis is to review relevant medical records and test reports, explain the procedure and potential risks to the couple, and take consent for the amniocentesis procedure.
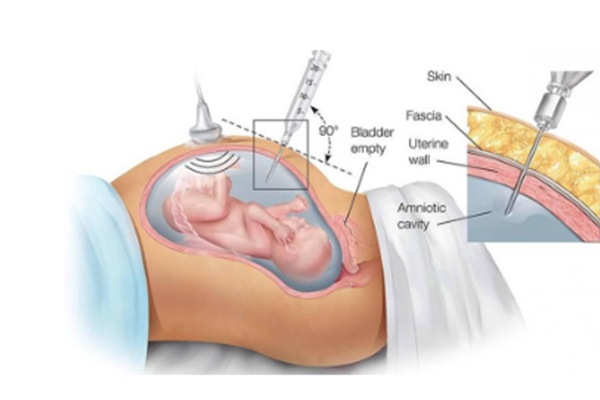
c) The Radiologist will use ultrasound guidance to locate the position of the needle.
d) Once the optimal spot is identified, a small dose of local anaesthesia is given to numb the area.
e) A thin long needle is gently inserted through the mother’s abdomen into the amniotic sac.
f) After confirming the needle position, around 20ml of amniotic fluid is withdrawn using a syringe, carefully avoiding contact with the fetus.
g) Then the needle is removed, and a small bandage is placed over the puncture site.
a) After the procedure, the amniotic fluid is sent to the laboratory for further analysis like FISH, Karyotyping, Microarray tests, etc., depending upon the problem suspected in the unborn baby.
b) The lab tests can provide vital information on chromosomal abnormalities, genetic disorders, neural tube defects, and certain metabolic conditions.
c) After the procedure, the mother is observed for a few minutes, and a TT injection is administered to the mother if necessary.
d) The lab results usually take about 4 to 15 days, depending on the type of test advised.